Extensive characterization of choline chloride and its solid–liquid equilibrium with water†
Abstract
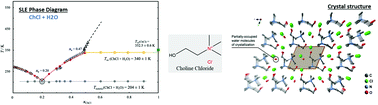
The importance of choline chloride (ChCl) is recognized due to its widespread use in the formulation of deep eutectic solvents. The controlled addition of water in deep eutectic solvents has been proposed to overcome some of the major drawbacks of these solvents, namely their high hygroscopicities and viscosities. Recently, aqueous solutions of ChCl at specific mole ratios have been presented as a novel, low viscous deep eutectic solvent. Nevertheless, these proposals are suggested without any information about the solid–liquid phase diagram of this system or the deviations from the thermodynamic ideality of its precursors. This work contributes significantly to this matter as the phase behavior of pure ChCl and (ChCl + H2O) binary mixtures was investigated by calorimetric and analytical techniques. The thermal behavior and stability of ChCl were studied by polarized light optical microscopy and differential scanning calorimetry, confirming the existence of a solid–solid transition at 352.2 ± 0.6 K. Additionally, heat capacity measurements of pure ChCl (covering both ChCl solid phases) and aqueous solutions of ChCl (xChCl < 0.4) were performed using a heat-flow differential scanning microcalorimeter or a high-precision heat capacity drop calorimeter, allowing the estimation of a heat capacity change of (ChCl) ≈ 39.3 ± 10 J K−1 mol−1, between the hypothetical liquid and the observed crystalline phase at 298.15 K. The solid–liquid phase diagram of the ChCl + water mixture was investigated in the whole concentration range by differential scanning calorimetry and the analytical shake-flask method. The phase diagram obtained for the mixture shows an eutectic temperature of 204 K, at a mole fraction of choline chloride close to xChCl = 0.2, and a shift of the solid–solid transition of ChCl–water mixtures of 10 K below the value observed for pure choline chloride, suggesting the appearance of a new crystalline structure of ChCl in the presence of water, as confirmed by X-ray diffraction. The liquid phase presents significant negative deviations to ideality for water while COSMO-RS predicts a near ideal behaviour for ChCl.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...