On relaxation and vibrational dynamics in the thermodynamic states of a chiral smectogenic glass-former†
Abstract
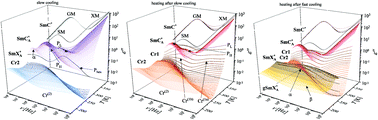
This article shows the full characteristics (i.e., the phase situation as well as the relaxation and vibrational dynamics) of the (S)-4′-(1-methyloctyloxycarbonyl)biphenyl-4-yl 4-[5-(2,2,3,3,4,4,4-heptafluorobutoxy)pentyl-1-oxy]-benzoate chiral liquid crystal. Besides two enantiotropic chiral smectic phases (SmC* and 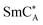 ), the compound under study also forms the hexatic smectic
), the compound under study also forms the hexatic smectic 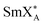 phase and two crystal phases (Cr1 and Cr2). The XRD patterns imply a similar structure of both crystal phases. The sample crystallizes upon slow cooling, while the
phase and two crystal phases (Cr1 and Cr2). The XRD patterns imply a similar structure of both crystal phases. The sample crystallizes upon slow cooling, while the 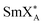 phase undergoes a glass transition during fast cooling. Upon subsequent heating, cold crystallization is observed. Our research reveals the complex relaxation dynamics in the identified thermodynamic states, e.g., two relaxations up to the beginning of cold crystallization, three modes in the crystal phases and seven processes in all smectic phases. The results from the scaling of the dielectric response indicate that the origin of the dynamics and behavior of the dielectric permittivity is the same for all phases, regardless of the change in temperature and/or external biasing field. The high value of the fragility index (mf ≈ 146) indicates that the compound under study is a fragile glass-forming system. The region of the –COO– and –COC– group stretching vibrations is primarily sensitive to the structural changes occurring during phase transitions.
phase undergoes a glass transition during fast cooling. Upon subsequent heating, cold crystallization is observed. Our research reveals the complex relaxation dynamics in the identified thermodynamic states, e.g., two relaxations up to the beginning of cold crystallization, three modes in the crystal phases and seven processes in all smectic phases. The results from the scaling of the dielectric response indicate that the origin of the dynamics and behavior of the dielectric permittivity is the same for all phases, regardless of the change in temperature and/or external biasing field. The high value of the fragility index (mf ≈ 146) indicates that the compound under study is a fragile glass-forming system. The region of the –COO– and –COC– group stretching vibrations is primarily sensitive to the structural changes occurring during phase transitions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...