A simulation study on the subdiffusion of polymer chains in crowded environments containing nanoparticles†
Abstract
Polymer chains in crowded environments often show subdiffusive behavior. We adopt molecular dynamics simulations to study the conditions for the subdiffusion of polymer chains in crowded environments containing randomly distributed, immobile, attractive nanoparticles (NPs). The attraction is strong enough to adsorb polymer chains on NPs. The results show that subdiffusion occurs at a low concentration of polymer chains (cp). A transition from subdiffusion to normal diffusion is observed when cp exceeds the transition concentration 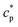 , which increases with increasing concentration of NPs while decreases with increasing size of NPs. The high concentration and small size of NPs exert a big effect on the subdiffusion of polymer chains. The subdiffusive behavior of polymer chains can be attributed to the strong adsorption of polymer chains on the attractive NPs. For the subdiffusion case, polymer chains are adsorbed strongly on multiple NPs, and they diffuse via the NP-exchange diffusion mechanism. However for the normal diffusion case, polymer chains are either free or weakly adsorbed on one or a few NPs, and they diffuse mainly via the adsorption-and-desorption diffusion mechanism.
, which increases with increasing concentration of NPs while decreases with increasing size of NPs. The high concentration and small size of NPs exert a big effect on the subdiffusion of polymer chains. The subdiffusive behavior of polymer chains can be attributed to the strong adsorption of polymer chains on the attractive NPs. For the subdiffusion case, polymer chains are adsorbed strongly on multiple NPs, and they diffuse via the NP-exchange diffusion mechanism. However for the normal diffusion case, polymer chains are either free or weakly adsorbed on one or a few NPs, and they diffuse mainly via the adsorption-and-desorption diffusion mechanism.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...