Development of the first non-hydroxamate selective HDAC6 degraders†
Abstract
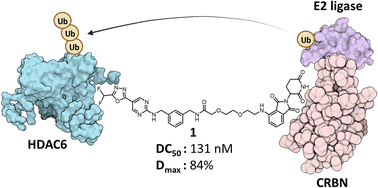
The targeted degradation of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) by heterobifunctional degraders constitutes a promising approach to treat HDAC6-driven diseases. Previous HDAC6 selective degraders utilised a hydroxamic acid as a zinc-binding group (ZBG) which features mutagenic and genotoxic potential. Here we report the development of a new class of selective HDAC6 degraders based on a difluoromethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole warhead as ZBG.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...