Imaging of antitubercular dimeric boronic acids at the mycobacterial cell surface by click-probe capture†
Abstract
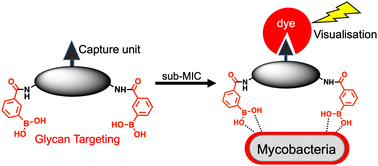
Dimeric boronic acids kill Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) by targeting mycobacterial specific extracellular glycans, removing the requirement for a therapeutic agent to permeate the complex cell envelope. Here we report the successful development and use of new ‘clickable’ boronic acid probes as a powerful method to enable the direct detection and visualisation of this unique class of cell-surface targeting antitubercular agents.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2022 Pioneering Investigators


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...