Epoxidation vs. dehydrogenation of allylic alcohols: heterogenization of the VO(acac)2 catalyst in a metal–organic framework†
Abstract
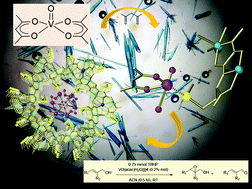
Allylic alcohol epoxidation and dehydrogenation reactivity is distinguished when VO(acac)2 is used in solution or anchored in a metal–organic framework (MOF). The chemical mechanism depends on the electronic profile of alkene substituents when the vanadyl complex is used in the homogenous phase. However, confinement effects imparted by MOF channels allow gaining control of the chemoselectivity toward the dehydrogenation product.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Communications HOT Articles 2022


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...