Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of peptide nucleic acid probes with improved interstrand-crosslinking abilities: application to biotin-mediated RNA-pulldown†
Abstract
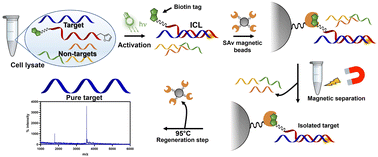
The development of interstrand-crosslinking (ICL) probes for the covalent targeting of DNA and RNA sequences of interest has been extensively reported in the past decade. However, most of the reactions reported so far induce the formation of a stable adduct that cannot be reverted, thus rendering these chemistries less useful in applications where the reversibility of the reaction is needed for further downstream processing of the targeted and isolated sequences, such as enzymatic amplification steps. In this work, we report on the reversibility of the furan-mediated ICL reaction. ICL formation can be conveniently triggered by either chemical (N-bromo succinimide, NBS) or luminous stimuli (visible light irradiation in presence of a photosensitizer) and quantitative reversion can be achieved by heating the crosslinked sample at 95 °C, while maintaining the structure of the DNA/RNA targets intact. As a proof-of-concept and showing the benefits of the ICL reversibility, we apply furan-mediated ICL to the pulldown of a target RNA strand from cell lysate.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Themed collection on XNA Xeno-nucleic acids


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...