Enhanced human T cell expansion with inverse opal hydrogels†
Abstract
Advanced personalized immunotherapies still have to overcome several biomedical and technical limitations before they become a routine cancer treatment in spite of recent achievements. In adoptive cell therapy (ACT), the capacity to obtain adequate numbers of therapeutic T cells in the patients following ex vivo treatment should be improved. Moreover, the time and costs to produce these T cells should be reduced. In this work, inverse opal (IOPAL) 3D hydrogels consisting of poly(ethylene) glycol (PEG) covalently combined with heparin were engineered to resemble the environment of lymph nodes, where T cells get activated and proliferate. The introduction of an IOPAL strategy allowed a precise control on the porosity of the hydrogels, providing an increase in the proliferation of primary human CD4+ T cells, when compared with state-of-the-art expansion systems. Additionally, the IOPAL hydrogels also showed a superior expansion compared to hydrogels with the same composition, but without the predetermined pore structure. In summary, we have shown the beneficial effect of having an IOPAL architecture in our 3D hydrogels to help achieving large numbers of cells, while maintaining the desired selected phenotypes required for ACT.
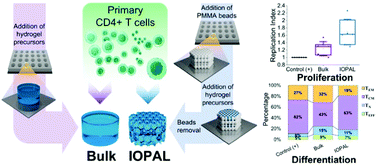
- This article is part of the themed collections: Biomaterials Science Recent HOT Articles and 31st Annual Conference of the European Society of Biomaterials


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...