Selective and ultrasensitive citric acid assay in urine samples using a MWCNT/Fe3O4 nanoparticle-modified carbon paste electrode
Abstract
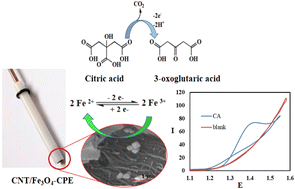
A carbon paste electrode (CPE) modified with multiwalled carbon nanotubes and magnetite nanoparticles is introduced (CNT/Fe3O4-CPE) as the most sensitive citric acid (CA) electrochemical sensor reported so far. The structural and spectroscopic characterization by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Raman spectroscopy is presented. The electrocatalytic performance of the electrode was substantiated using cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Performing voltammetric experiments at different pH values and various scan rates gave some evidence for the electro-oxidation mechanism of CA. The EIS study gave an obvious indication for the enhancement of the charge transfer rate of CA by the nanocomposite. Various parameters affecting the electrode performance were studied. Using differential pulse voltammetry it was found that the CNT/Fe3O4-CPE showed a linear dynamic range of 5.0 × 10−7–1 × 10−4 mol L−1, an excellent sensitivity of 5184 μA mM−1 cm−2, and a detection limit of 3.6 × 10−7 mol L−1 for CA determination. The relative standard deviation was found to be 3.1% (n = 3). The method was utilized for CA determination in urine samples without utilizing complicated sample pretreatment.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analytical Methods HOT Articles 2022


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...