Derivatization-assisted immunoassays: application for group-specific detection of potent methamphetamine and amphetamine enantiomers†
Abstract
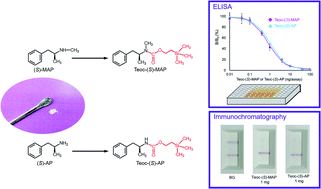
Reliable and feasible tools for detecting (S)-methamphetamine [(S)-MAP] and (S)-amphetamine [(S)-AP] are required for regulating their illicit circulation. Antibodies that react equally to these stimulants are desirable for this purpose, but have been difficult to generate because of the crucial difference between their characteristic structures: i.e., N-methylamino (MAP) and amino (AP) groups. Furthermore, their small molecular masses (Mr < 150) have hampered the generation of high-affinity antibodies. To overcome these problems, we converted (S)-MAP and -AP into their 2-(trimethylsilyl)ethyl carbamate forms, Teoc-(S)-MAP and -AP, respectively, as surrogate analytes. The Teoc-derivatization not only increases their molecular masses, but also masks their structural differences. We generated a novel monoclonal antibody that showed a satisfactory affinity to Teoc-(S)-MAP residues (Kd = 13 nM as the IgG form) and developed a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using microplates containing immobilized Teoc-(S)-MAP residues. Almost overlapping dose–response curves were obtained for Teoc-(S)-MAP and -AP, with the limit of detection of 0.078 and 0.10 ng per assay, respectively. A fixed amount of test powder sample (1 mg) was derivatized with Teoc-O-succinimidyl for 5 min, and subjected to ELISA using Teoc-(S)-MAP as the calibration standard. Under this protocol, (S)-MAP and -AP were converted to their Teoc derivatives with 30% and 34% yield, respectively, determined using ELISA as “Teoc-(S)-MAP equivalent,” being distinguished from the derivatization products of (R)-MAP, (R)-AP, ephedrine, (S)-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, tyramine, dopamine, and β-alanine. This ELISA detected as little as 10 μg of (S)-MAP and -AP, and (S)-MAP in urine obtained from (S)-MAP-administered rats. Immunochromatography devices were also developed using gold nanoparticles coated with the monoclonal antibody, with which 0.10 mg of (S)-MAP and -AP was detected by the naked eye. We conclude that the present derivatization-assisted immunoassays may be useful for the detection of (S)-MAP and/or -AP in early stage screening of suspicious substances.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analytical Methods HOT Articles 2022


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...