Core–shell copper-gold nanoparticles modified at the boron-doped diamond electrode for oxygen sensors†
Abstract
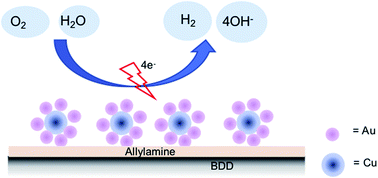
Bimetallic copper–gold (Cu@Au) nanoparticles were synthesized and utilised to modify boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrodes. Nanorod particles with a diameter size of around 10 nm and a length of around 20 nm were successfully synthesized. These nanoparticles were then attached to the BDD surface by using allylamine as the bridge. Comparison among the BDD modified with Cu@Au and individual gold nanoparticles showed that Cu@Au nanoparticles created around 3 times higher gold coverage on the BDD surface than normal gold nanoparticles. It was also found that the use of allylamine as the bridge can attach more gold than copper nanoparticles. Moreover, around two times higher current responses of oxygen reduction reaction were observed at Cu@Au-modified BDD. Good linearity in a concentration range from 2 to 9 ppm could be achieved with a sensitivity of 0.0138 mA ppm−1 and limit detection of 1.98 ppm. An application of the modified BDD for a biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) sensor using Rhodotorula mucilaginosa UICC Y-181 as the biosensing agent was also demonstrated with glucose solutions as the solution model. Sensitivity equivalent to 17.4 μA mM−1 BOD could be achieved. The system showed good stability with an RSD of 3.45% in 10 measurements.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...