A cascade Fermat spiral microfluidic mixer chip for accurate detection and logic discrimination of cancer cells†
Abstract
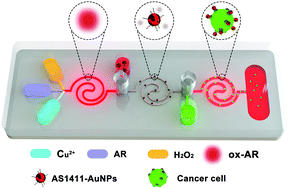
Since cancer has emerged as one of the most serious threats to human health, the highly sensitive determination of cancer cells is of significant importance to improve the accuracy of early clinical diagnosis. In our investigation, a novel cascade Fermat spiral microfluidic mixer chip (CFSMMC) combined with fluorescence sensors as a point-of-care (POC) testing system is successfully fabricated to detect and differentiate cancer cells (MCF-7) from normal cells with excellent sensitivity and selectivity. Here, copper ions (Cu2+) with peroxidase properties can catalyze the oxidation of the non-fluorescent substrate Amplex Red (AR) to the highly fluorescent resorufin (ox-AR) in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Subsequently, thanks to the quenching response of AS1411-AuNPs to ox-AR in the microchannel and the binding of AS1411 to nucleolin on the surface of cancer cells, a CFSMMC-based POC system is established for the highly sensitive detection and identification of human breast cancer cells in a “turn on” manner. The change in fluorescence intensity is linearly related to the concentration of MCF-7, ranging from 102 to 107 cells per mL with a limit of detection (LOD) as low as 17 cells per mL. Interestingly, the cascaded AND logic gate is integrated with CFSMMC for the first time to distinguish cancer cells from normal cells under the control of logic functions, which exhibits great potential in the development of one-step rapid and intelligent detection and logic discrimination.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...