Pico-molar electrochemical detection of ciprofloxacin at composite electrodes†
Abstract
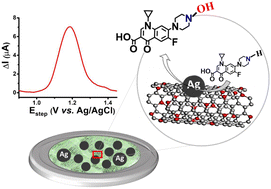
Rapid determination of antibiotic residues is crucial for both environmental monitoring and the ecosystem. The presented study explores the development of a sensitive, selective, and highly reproducible chemical sensor to detect the antibiotic ciprofloxacin (Cip) in 0.1 M NaNO3 and in tap water. The designed sensor was constructed using oxygen functionalized carbon nanotubes (OCNTs), a layer of conductive polymer (polydopamine; PDA), and electro-deposited silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) at a glassy carbon electrode. Double-pulse electro-deposition was employed, as it offers numerous advantages including quick analysis time (s, ms), high reproducibility, and does not require expensive complexing agents, even at room temperature. The fabricated chemical sensor was fully optimized and characterized using physiochemical and electrochemical techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and voltammetry. Electrochemical measurements demonstrate high applicability of the chemical sensor towards the detection of Cip in the pico-molar concentration range. Detection and quantification levels were determined and the stability of the sensor was assessed. The obtained results demonstrate the potential of the OCNTs-PDA-Ag sensor to detect Cip in environmental samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...