Prediction of the photoelectrochemical performance of hematite electrodes using analytical data
Abstract
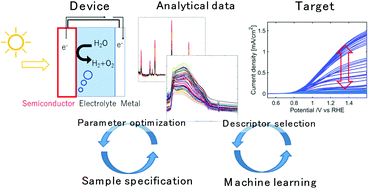
Machine learning (ML) has been extensively utilized in various fields of chemistry, such as molecular design and optimization of the fabrication parameters of the material. However, there is still a difficulty in applying ML for devices/materials fabricated in a lab because plenty of data for accurate calculation are difficult to obtain due to the limited number of samples. As a promising energy-harvesting material, we have studied hematite electrodes for photocatalytic water splitting. Herein, we have examined the critical factors affecting the photoelectrochemical (PEC) performance by applying ML for a limited number of fabricated electrodes to reveal the origin of poor reproducibility of the performance. To find the dominant factors affecting the PEC performance, the feature values were directly extracted from analytical data such as X-ray diffraction, Raman, UV/vis and photoelectrochemical impedance spectroscopy (PEIS) measurements. The dominant factors for the performance were identified from the prediction analysis of the performance by ML. Two types of descriptors were examined; all the analytical data were included and those without the PEIS data, which had a high correlation with the photocurrent. The determination coefficients (R2) of the prediction accuracy were >0.8 in both cases and the dominant features were identified for the improvement of PEC performance without any prior knowledge.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...