A primer extension activating 3D DNAzyme walker for in situ imaging and sensitive detection of telomerase activity†
Abstract
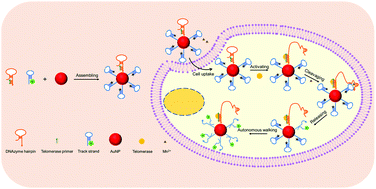
Acquiring information on telomerase activity at multiple levels contributes to a better understanding of its role in various physiological and pathological processes. Herein, a primer extension activating 3D DNAzyme walker is developed for in situ imaging and sensitive detection of telomerase activity. This walker is constructed via co-modifying specially designed hairpin structured walking strands and track strands on a gold nanoparticle (AuNP). The walking strand contains a pre-blocked DNAzyme sequence and a telomerase primer hybridized to its root. The track strand embeds at an RNA cleavage site and is labeled with the FAM group. After this walker is taken up by cells, the telomerase primer is extended under the action of endogenous telomerase to liberate DNAzyme. The liberated DNAzyme cuts track strands in the presence of the cofactor Mn2+ to drive the walker's processive operation, resulting in an enhanced fluorescence recovery of the AuNP-quenched FAM fluorophore. In situ imaging of telomerase activity in three different cell lines (MCF-7 cells, HeLa cells and HL-7702 cells) was well implemented. The discrimination of cancer cells from normal cells and the screening of telomerase inhibitors have been achieved. The sensitive detection of telomerase activity in HeLa cell lysate has also been realized with a detection limit of 10 cells. This walker performed a new approach for monitoring telomerase activity from different levels, providing a potential tool for clinical diagnosis, prognostic evaluation and drug screening.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...