Bioelectrocatalytic methanol production with alcohol dehydrogenase using methylviologen as an electron mediator
Abstract
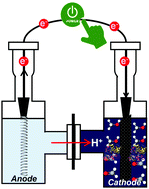
Methanol fuel is paid much attention as an alternative lower carbon fuel for internal combustion and other engines. In this work, the bioelectrocatalytic methanol production from formaldehyde with alcohol dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ADH) using methylviologen (MV2+) as an electron mediator was developed toward establishing a method for synthesizing CO2 to methanol. When a single-electron reduction potential of MV2+ (−700 mV vs. Ag/AgCl electrode as a reference) was applied in the presence of ADH, reduction of formaldehyde to methanol was observed. After 90 min continuous external bias of −700 mV, 22.6% formaldehyde consumption based on methanol production was observed in this bioelectric catalyst system.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...