A flexible thin film lithium battery with a chemical vapor deposited organic complex cathode†
Abstract
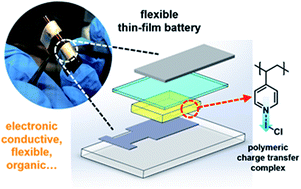
Organic cathode materials have attracted significant research attention recently, yet their low electronic conductivity limits their application as solid-state cathodes in lithium batteries. This work describes the development of a novel organic cathode chemistry with significant intrinsic electronic conductivity for solid-state thin film batteries. A polymeric charge transfer complex (CTC) cathode, poly(4-vinylpyridine)-iodine monochloride (P4VP·ICl), was prepared by initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD). Critical chemical, physical, and electrochemical properties of the CTC complex were characterized. The complex was found to have an electronic conductivity of 4 × 10−7 S cm−1 and total conductivity of 2 × 10−6 S cm−1 at room temperature, which allows the construction of a 2.7 μm thick dense cathode. By fabricating a P4VP·ICl|LIPON|Li thin film battery, the discharge capacity of P4VP·ICl was demonstrated to be >320 mA h cm−3 on both rigid and flexible substrates. The flexible P4VP·ICl|LIPON|Li battery was prepared by simply replacing the rigid substrate with a flexible polyimide substrate and the as-prepared battery can be bent 180° while maintaining electrochemical performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...