Conjugated polymers with controllable interfacial order and energetics enable tunable heterojunctions in organic and colloidal quantum dot photovoltaics†
Abstract
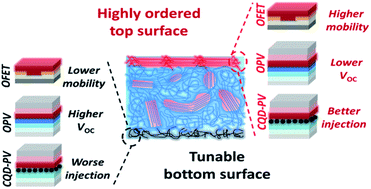
Conjugated polymers are widely used as photoactive and transport layers in organic and hybrid photovoltaics (PV), where the energetics of polymers are a key design criterion. Here, we show that significant variations in terminal molecular ordering between top and bottom surfaces of a wide range of conjugated polymer films can result in sizable interfacial ionization energy (IE) differences by as much as 0.33 eV, which has significant impact on organic and hybrid PV devices. Such tunability is surprisingly seen even in nominally amorphous polymers. We devise a strategy leveraging wet and dry laminations to form donor–acceptor planar heterojunction (PHJ) devices using exposed and buried surfaces of donor polymers and demonstrate meaningful influence over the open circuit voltage (VOC) by up to 0.32 V. We use this insight to devise a controlled intermixing approach which yields superior VOC and JSC to conventional bulk heterojunction devices by leveraging the disordered interface to maximize VOC and the greater aggregation of the donor to increase the JSC. We go on to demonstrate how judicious control of polymer surface IE benefits charge extraction in colloidal quantum dot PV devices in the role of hole transport layers. Our results show that polymer interfacial and bulk properties are both critical to the functionality of optoelectronic devices and should both be given prime consideration when designing heterojunction devices.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
