Inverse potential scaling in co-electrocatalytic activity for CO2 reduction through redox mediator tuning and catalyst design†
Abstract
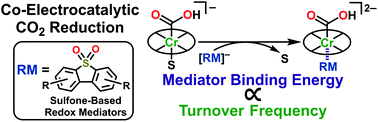
Electrocatalytic CO2 reduction is an attractive strategy to mitigate the continuous rise in atmospheric CO2 concentrations and generate value-added chemical products. A possible strategy to increase the activity of molecular systems for these reactions is the co-catalytic use of redox mediators (RMs), which direct reducing equivalents from the electrode surface to the active site. Recently, we demonstrated that a sulfone-based RM could trigger co-electrocatalytic CO2 reduction via an inner-sphere mechanism under aprotic conditions. Here, we provide support for inner-sphere cooperativity under protic conditions by synthetically modulating the mediator to increase activity at lower overpotentials (inverse potential scaling). Furthermore, we show that both the intrinsic and co-catalytic performance of the Cr-centered catalyst can be enhanced by ligand design. By tuning both the Cr-centered catalyst and RM appropriately, an optimized co-electrocatalytic system with quantitative selectivity for CO at an overpotential (η) of 280 mV and turnover frequency (TOF) of 194 s−1 is obtained, representing a three-fold increase in co-catalytic activity at 130 mV lower overpotential than our original report. Importantly, this work lays the foundation of a powerful tool for developing co-catalytic systems for homogeneous electrochemical reactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...