Exploring novel heterojunctions based on the cerium metal–organic framework family and CAU-1, as dissimilar structures, for the sake of photocatalytic activity enhancement†
Abstract
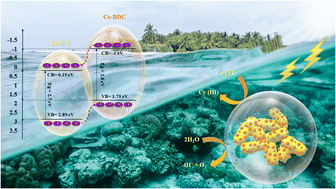
Ce-based metal–organic frameworks (Ce-MOFs) are excellent photocatalysts due to their high efficiency in charge transportation. The integration of this family with CAU-1 (CAU standing for Christian-Albrechts-University), as a MOF benefiting from its ultra-high surface area, can remarkably enhance the properties of the structure. This research includes four new heterojunctions, namely CAU-1/Ce-BDC–NH2, CAU-1/Ce-UiO-66, CAU-1/Ce-MOF-808, and CAU-1/Ce-BDC, prepared by an innovative method, and several characterization techniques were employed to study the structural features of the frameworks. Their high surface area and low bandgap energy seemed appropriate for catalytic applications. Therefore, CAU-1/Ce-BDC was chosen for the photocatalytic removal of Cr(VI), a dangerous heavy metal, from aqueous systems. According to the results, a 96% reduction of Cr(VI) to Cr(III) within 75 min was observed, and the catalyst retained its stability after four runs of reactions under acidic conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...