Controlled growth of ZnO nanoparticles using ethanolic root extract of Japanese knotweed: photocatalytic and antimicrobial properties†
Abstract
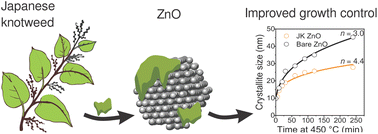
Synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (NPs) was mediated by plant extracts to assist in the reduction of zinc atoms during the synthesis and act as a capping agent during annealing. The preparation used ethanolic extracts from the roots of Japanese knotweed (Fallopia japonica). Two major outcomes could be made. (i) A synergistic effect of multiple polyphenolic components in the extract is needed to achieve the capping effect of crystallite growth during thermal annealing at 450 °C characterized by an exponential growth factor (n) of 4.4 compared to n = 3 for bare ZnO. (ii) Synergism between the ZnO NPs and plant extracts resulted in superior antimicrobial activity against both Gram-positive bacteria, e.g., Staphylococcus aureus, and Gram-negative bacteria, e.g., Escherichia coli and Campylobacter jejuni. The materials were also tested for their antimicrobial activity against S. aureus under ultraviolet (UV) illumination. Also here, the photocatalyst prepared with plant extracts was found to be superior. The residues of the plant extract molecules on the surface of the catalyst were identified as the main cause of the observed differences, as proved by thermal gravimetry. Such a preparation using ethanolic extract of Fallopia japonica could serve as a more controlled synthesis of ZnO and potentially other metal oxides, with low environmental impact and high abundance in nature.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...