Exploration of expanded carbohydrate chemical space to access biological activity using microwave-induced acid condensation of simple sugars†
Abstract
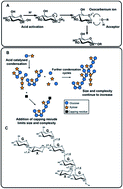
Complex glycans are ubiquitous in nature and essential to life. Despite their diverse roles, however, only a fraction of their potential chemical space has been explored. New regions of this chemical space can, nevertheless, be accessed by generating structures that do not occur in nature or by modifying naturally-occurring polysaccharide structures – collectively, termed new polysaccharides (NPs). Two synthetic routes to NPs are described; the de novo route, directly from monosaccharide starting materials and the functionalization route, involving glycosylation of existing polysaccharides. The reaction involves a simple condensation step under microwave heating, catalysed by environmentally benign organic acids and is illustrated by the generation of structures with biological activities ranging from cell signalling and inhibition of bacterial growth, to mimicking carbohydrate antigens of pathogenic microorganisms. The method is as applicable to fine chemicals as it is to industrial waste, for example, biotechnologically-derived D-allulose (D-psicose), or the waste products of biofermentation. Accessing this chemical space unlocks new functionalities, generating complex glycans with applications in the biological, medical, biotechnological and materials science arenas.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...