A strong hydride donating, acid stable and reusable 1,4-dihydropyridine for selective aldimine and aldehyde reductions†
Abstract
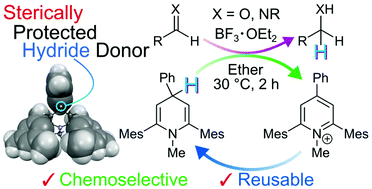
A 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative, lacking carbonyl groups and containing bulky aryl substituents, was synthesized and found to have a high hydride donating ability, acid resistance and reusability. Thermodynamic parameters for electron and hydride transfer in the redox system comprising the 1,4-dihydropyridine and its corresponding pyridinium ion were determined. In addition, studies showed that the 1,4-dihydropyridine with steric hindrance can be used to promote efficient, boron trifluoride catalyzed selective reduction reactions of aldimines and aldehydes under mild conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...