Synthesis of micro- and nanosheets of CrCl3–RuCl3 solid solution by chemical vapour transport†
Abstract
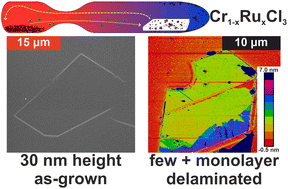
Solid solutions of 2D transition metal trihalides are rapidly growing in interest for the search for new 2D materials with novel properties at nanoscale dimensions. In this regard, we present a synthesis method for the Cr1−xRuxCl3 solid solution and describe the behaviour of the unit cell parameters over the whole composition range, which in general follows Vegard's law in the range of a = 5.958(6)CrCl3 … 5.9731(5)RuCl3 Å, b = 10.3328(20)CrCl3 … 10.34606(21)RuCl3 Å, c = 6.110(5)CrCl3 … 6.0385(5)RuCl3 Å and β = 108.522(15)CrCl3 … 108.8314(14)RuCl3 °. The synthesized solid solution powder was subsequently used to deposit micro- and nanosheets directly on a substrate by applying chemical vapour transport in a temperature gradient of 575 °C → 525 °C for 2 h and 650 °C → 600 °C for 0.5 h as a bottom-up approach without the need for an external transport agent. The observed chromium chloride enrichment of the deposited crystals is predicted by thermodynamic simulation. The results allow for a nanostructure synthesis of this solid solution with a predictable composition down to about 30 nm in height and lateral size of several μm. When applying a quick consecutive delamination step, it is possible to obtain few- and monolayer structures, which could be used for further studies of downscaling effects for the CrCl3–RuCl3 solid solution. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and Raman spectroscopy were used to confirm the purity and quality of the synthesized crystals.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...