Combinatorial nanodroplet platform for screening antibiotic combinations†
Abstract
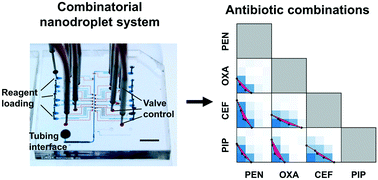
The emergence and spread of multidrug resistant bacterial strains and concomitant dwindling of effective antibiotics pose worldwide healthcare challenges. To address these challenges, advanced engineering tools are developed to personalize antibiotic treatments by speeding up the diagnostics that is critical to prevent antibiotic misuse and overuse and make full use of existing antibiotics. Meanwhile, it is necessary to investigate novel antibiotic strategies. Recently, repurposing mono antibiotics into combinatorial antibiotic therapies has shown great potential for treatment of bacterial infections. However, widespread adoption of drug combinations has been hindered by the complexity of screening techniques and the cost of reagent consumptions in practice. In this study, we developed a combinatorial nanodroplet platform for automated and high-throughput screening of antibiotic combinations while consuming orders of magnitude lower reagents than the standard microtiter-based screening method. In particular, the proposed platform is capable of creating nanoliter droplets with multiple reagents in an automatic manner, tuning concentrations of each component, performing biochemical assays with high flexibility (e.g., temperature and duration), and achieving detection with high sensitivity. A biochemical assay, based on the reduction of resazurin by the metabolism of bacteria, has been characterized and employed to evaluate the combinatorial effects of the antibiotics of interest. In a pilot study, we successfully screened pairwise combinations between 4 antibiotics for a model Escherichia coli strain.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...