The different effects of psyllium husk and orlistat on weight control, the amelioration of hypercholesterolemia and non-alcohol fatty liver disease in obese mice induced by a high-fat diet†
Abstract
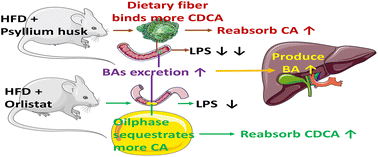
Obesity is a widespread medical problem, for which many drugs have been developed, each with its own limitations. Orlistat, a lipase inhibitor, functions as a fat absorption blocker and is a widely used over-the-counter drug in China. Psyllium husk, in contrast, is a food source rich in dietary fibre and is beneficial for weight loss because it reduces appetite. Here, it was investigated how psyllium husk treatments affect mice with a high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity, using obesity-related indices, metabolism indices, and gut microbiota, compared to orlistat treatments. Orlistat had a greater effect on weight loss, whereas psyllium husk had a greater effect at reducing serum and liver cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Treatments had similar effects on controlling the body fat rate, the expression level of farnesoid X receptor, sterol 27-hydroxylase and oxysterol 7-hydroxylase (CYP7B1) in the liver, and the regulation of major bile acids such as cholic acid, chenodeoxycholic acid, deoxycholic acid, and lithocholic acid in faecal content. However, the expression of CYP7A1 in the liver and the structures of faecal bile acids were different between the two drugs. Furthermore, although they also had similar effects on the gut microbiota at the phylum level, there were differences at the genus level for Roseburia, Bacteroides, Faecalibacterium, Coprobacillus, and Akkernansia, which led to the difference in the serum lipopolysaccharide (LPS) level. Orlistat increased the food intake of the obese mice that were fed a HFD, which led to an increase in water intake, serum triglyceride levels, and lower glucose tolerance. Although orlistat is considered a suitable drug for weight loss, psyllium husk is a comparatively more cost-effective choice for ameliorating hypercholesterolemia and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease caused by a HFD.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...