Evaluation of novel nutraceuticals based on the combination of oat beta-glucans and a green coffee phenolic extract to combat obesity and its comorbidities. A randomized, dose–response, parallel trial
Abstract
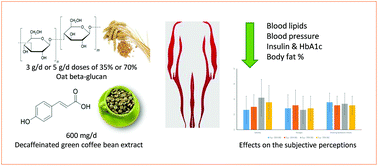
Obesity and its associated comorbidities are a major public health concern worldwide. Reduced energy intake and increased physical activity interventions have limited success in the long term. Nutraceuticals might be an alternative means to help lose weight and reduce obesity-associated cardiometabolic risk factors without changes in the habitual diet. The objective of the present study was to comparatively evaluate the efficiency of nutraceuticals based on the combination of a decaffeinated green coffee bean extract (GCBE) and two types of oat beta-glucans (BG) with different physiochemical properties on obesity related biomarkers in overweight/obese subjects. A randomized, dose–response, parallel, blind study was carried out in four groups of subjects (n = 15 each) who consumed for 6 weeks, twice a day, a nutraceutical containing 3 g d−1 or 5 g d−1 doses of 35% or 70% BG and a fixed amount of GCBE providing 600 mg d−1 of phenols. 35% BG showed a 10 and 100 times higher molecular weight and viscosity, respectively, compared to 70% BG. Food intake, anthropometry and different cardiometabolic markers were assessed at the beginning and end of the intervention. According to the general model of variance with repeated measure analysis, the intervention caused positive changes in the levels of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, VLDL cholesterol, triglycerides, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, haemoglobin A1c, insulin, systolic blood pressure (SBP), total body fat percentage (TBF%), visceral fat percentage, and waist and hip circumferences without differences among the treatments, except for SBP and TBF%. Looking into the rates of change [(end value − beginning value)/beginning value] of these parameters, 5 g – 70% BG was the treatment that lowered TBF% the most. In conclusion, 5 g – 70% BG may be more effective in helping to lose weight and additionally, it produced the least bloating according to participants’ subjective perception.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...