Combined effects of emitter–emitter and emitter–plasmonic surface separations dictate photoluminescence enhancement in a plasmonic field†
Abstract
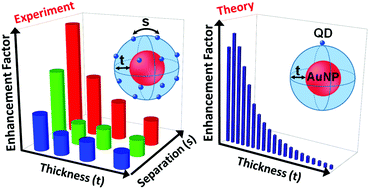
The brightness of an emitter can be enhanced by metal-enhanced fluorescence, wherein the excitonic dipole couples with the electromagnetic field of the surface plasmon. Herein, we experimentally map the landscape of photoluminescence enhancement (EFexp) of emitters in a plasmonic field as a function of the emitter–emitter separation, s, and the emitter–plasmon distance, t. We use Au nanoparticles overcoated with inert spacers as plasmonic systems and CdSe/ZnS quantum dots (QDs) as an emitter bearing opposite surface charges. The t and s are varied by changing the spacer thickness and number density of QDs on the plasmonic surface, respectively. The electrostatic binding of emitters on the plasmonic surface and their number density are established by following the variation of zeta-potential. EFexp is high, when t is short and s is large; nevertheless, it decreases when the emitter–emitter interaction dominates due to plasmon assisted nonradiative processes. In the absence of a plasmonic field, the enhancement observed is attributed to environmental effects and is independent of s, confirming the role of the electric field. Indeed, the distance dependence of EFexp closely follows the decay of the plasmonic field upon dilution of the emitter concentration on nanoparticles’ surface (s = 18 nm). The QD–plasmon system is visualized in the framework of the Thomson problem, and classical electrodynamics calculations give the trends in t and s dependence of the photoluminescence. Being the first report on the simultaneous dependence of t and s on plasmon-enhanced photoluminescence, the results presented herein will open newer opportunities in the design of hybrid systems with a high brightness.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...