In situ silane activation enables catalytic reduction of carboxylic acids†
Abstract
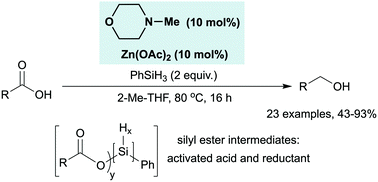
We describe a catalytic system for the conversion of carboxylic acids into alcohols using substoichiometric zinc acetate and N-methyl morpholine, in combination with phenylsilane as the nominal terminal reductant. Reaction monitoring by 19F NMR spectroscopy demonstrates that the reaction proceeds by mutual activation of the carboxylic acid and silane through the in situ generation of silyl ester intermediates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...