Green synthesis of broccoli-derived carbon quantum dots as effective photosensitizers for the PDT effect testified in the model of mutant Caenorhabditis elegans†
Abstract
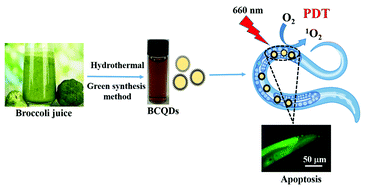
The clinical application of photodynamic therapy (PDT) is still limited because of the drawbacks of the traditional photosensitizers, such as low singlet oxygen (1O2) quantum yield and the problem of photobleaching. Herein, carbon quantum dots (CQDs) derived from broccoli natural biomass as a carbon source were fabricated via a simple hydrothermal method and showed outstanding PDT ability as an effective photodynamic agent tested in Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) models. The as-prepared broccoli-derived CQDs (BCQDs) showed excellent water solubility and optical properties and could generate singlet oxygen (1O2) effectively under irradiated light with a wavelength of 660 nm. The in vivo experiment revealed that the PDT efficiency of the BCQDs was dependent on the induction of germline apoptosis through the cep-1/p53 pathway. Further investigation confirmed the DNA damage of the worm by the BCQDs after sufficient light irradiation, which was tested by measuring the egl-1-fold induction in hus-1(op244), and cep-1(w40) mutants that have a loss of function in the genes involved in DNA damage response such as hus-1 (DNA checkpoint gene) and cep-1/p53 (tumor suppressor). The lack of germline apoptosis in the loss of function mutants egl-1(n487), hus-1(op244), and cep-1(w40) exposed to light irradiation compared with the control proved the necessity of these genes in DNA damage-induced germline apoptosis. Therefore, this work has not only provided a new photodynamic agent but also introduced C. elegans as an easy and high-throughput model for the rapid evaluation of the efficiency of PDT.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...