Characterization of glycerophospholipids at multiple isomer levels via Mn(ii)-catalyzed epoxidation†
Abstract
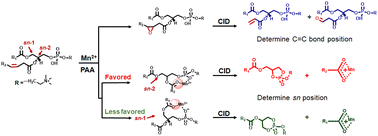
Characterization of glycerophospholipid isomers is of significant importance as they play different roles in physiological and pathological processes. In this work, we present a novel and bifunctional derivatization method utilizing Mn(II)-catalyzed epoxidation to simultaneously identify carbon–carbon double bond (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond)- and stereonumbering (sn)-positional isomers of phosphatidylcholine. Mn(II) coordinates with picolinic acid and catalyzes epoxidation of unsaturated lipids by peracetic acid. Collision-induced dissociation (CID) of the epoxides generates diagnostic ions that can be used to locate C
C bond)- and stereonumbering (sn)-positional isomers of phosphatidylcholine. Mn(II) coordinates with picolinic acid and catalyzes epoxidation of unsaturated lipids by peracetic acid. Collision-induced dissociation (CID) of the epoxides generates diagnostic ions that can be used to locate C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond positions. Meanwhile, CID of Mn(II) ion-lipid complexes produces characteristic ions for determination of sn positions. This bifunctional derivatization takes place in seconds, and the diagnostic ions produced in CID are clear and easy to interpret. Moreover, relative quantification of C
C bond positions. Meanwhile, CID of Mn(II) ion-lipid complexes produces characteristic ions for determination of sn positions. This bifunctional derivatization takes place in seconds, and the diagnostic ions produced in CID are clear and easy to interpret. Moreover, relative quantification of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond-and sn-positional isomers was achieved. The capability of this method in identifying lipids at multiple isomer levels was shown using lipid standards and lipid extracts from complex biological samples.
C bond-and sn-positional isomers was achieved. The capability of this method in identifying lipids at multiple isomer levels was shown using lipid standards and lipid extracts from complex biological samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...