Tremendously enhanced photocurrent enabled by triplet–triplet annihilation up-conversion for high-performance perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
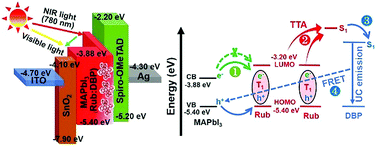
The limited solar spectrum utilization hinders the further amelioration of the performance of perovskite solar cells (PVSCs). An up-conversion (UC) process extends the spectral absorption of PVSCs from the visible to near-infrared (NIR) range and minimizes the sub-band-gap photon transmission loss. The perovskite-sensitized triplet–triplet annihilation (TTA) from rubrene (Rub) and dibenzotetraphenylperiflanthene (DBP) has shown great potential in UC applications. Herein, the TTA UC mechanism is introduced for the first time into PVSCs for converting NIR photons to visible photons, which facilitates the obvious improvement of photocurrent. Attributed to the TTA UC effect and energy band alignment of the Rub:DBP UC layer with the perovskite, the MAPbI3 based PVSCs acquire a champion power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 20.18% accompanied by significant enhancements in the short circuit current density (Jsc) and open-circuit voltage (Voc). In addition, rubrene doping can promote perovskite growth owing to the formation of π-conjugated agglomerates, which serve as the growing sites for perovskite crystallization nuclei. Furthermore, the Rub:DBP-based unencapsulated devices exhibit excellent moisture stability, and maintain more than 80% of the primitive PCE after 14 days of storage under air conditions (50–70% humidity, 25 °C).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...