Sulfur-doping tuning oxygen vacancies in ultrathin 2D Ni–V mixed metal oxides for exceptional oxidase mimic and antibacterial applications†
Abstract
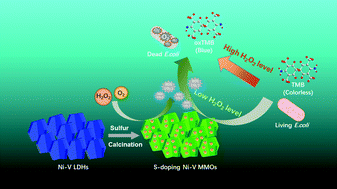
The development of effective and low-cost enzyme-like nanomaterials is an essential issue for antibacterial applications. Herein, novel ultrathin Ni–V mixed metal oxides (MMOs) doped with sulfur(S) were successfully designed. After calcination with S powder in a N2 atmosphere instead of in the air without S powder, the results proved that the obtained S-doping Ni–V MMOs remain ultrathin (5 nm in thickness) with much more vacancies and enhance oxidase (OXD) and peroxidase (POD) mimic activities sharply. More importantly, Ni–V MMO with a Ni/V molar ratio of 2 : 1 calcinated at 400 °C in the presence of sulfur shows the best OXD/POD mimic activity. The S-doping Ni–V MMOs also exhibit an antibacterial action on mode Gram-negative bacteria via generating ROS (mainly ˙O2−) in the presence of H2O2. It is also easily performed and highly specific. The unique 2D hierarchical nanostructure and sulfur doping endow the S-doping Ni–V MMO with abundant active sites and superb OXD/POD-like activity. The strategy expands the possibilities for boosting the catalytic activity of LDH-derived MMO nanomaterials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...