Ionic interactions control the modulus and mechanical properties of molecular ionic composite electrolytes†
Abstract
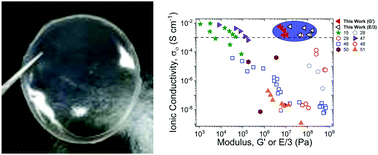
Molecular ionic composites (MICs) are a new class of solid electrolytes that combine ionic liquids (ILs) and a rigid-rod double helical polyelectrolyte, poly(2,2′-disulfonyl-4,4′benzidine terephthalamide) (PBDT). In this study, we focus on the mechanical, dielectric, and ion diffusive dynamics of MICs with a fixed PBDT weight percent (10 wt%) and varying IL chemistry and molecular volume (Vm). All six MICs produce tensile moduli in the range of 50–500 MPa at 30 °C, up to 60× higher than the shear moduli of the same MICs. The high range of moduli and tensile to shear modulus ratio emphasizes that the distribution of PBDT chains and the strong ionic interactions between IL ions and PBDT chains dictate the modulus and the mechanical strength in MICs. Additionally, these MICs exhibit high ionic conductivities ranging from 1–6 mS cm−1 at 30 °C, consistent with the measured diffusion coefficients of the IL ions. The tunability of the extraordinary mechanical properties and high ionic conductivities of MIC electrolytes greatly inspire their use in advanced electrochemical devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...