Small radius electron and hole polarons in PbX2 (X = F, Cl, Br) crystals: a computational study
Abstract
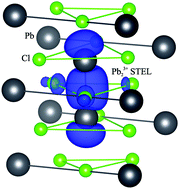
First-principles hybrid density functional theory (DFT) calculations were performed for small radius polarons – self-trapped electrons (STELs) and holes (STHs) in PbX2 (X = F, Cl, Br) crystals, widely used as parent materials for inorganic halide perovskites (CsPbX3) and scintillators. The atomic and electronic structures, spin and charge distributions and formation energies for both types of polarons were predicted for orthorhombic PbF2 and STELs for cubic PbF2. The STH structure was identified in a controversial case of PbCl2. We also confirmed and analyzed in detail experimentally suggested configurations for other cases. It is shown how, due to a delicate balance of ionic and covalent chemical bonding, hole localization changes from a single cation in fluorides and chlorides to an anion dimer in bromides. The positions of STEL/STH energy levels in the band gap were determined and discussed in conjunction with the role of spin–orbit effects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...