Coronene derivatives for transparent organic photovoltaics through inverse materials design†
Abstract
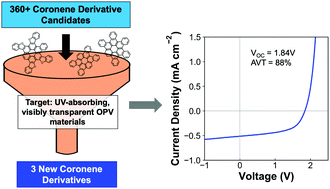
To accelerate materials discovery, computational methods such as inverse materials design have been proposed to predict the properties of target compounds of interest for specific applications. This in silico process can be used to guide subsequent synthesis and characterization. Inverse design is especially relevant for the field of organic molecules, for which there are nearly infinite synthetic modifications possible. With a target application of UV-absorbing, visibly transparent solar cells in mind, we calculated the orbital and transition energies of over 360 possible coronene derivatives. Our screening, or the constraints we imposed on the calculated series, resulted in the selection of three new derivatives, namely contorted pentabenzocoronene (cPBC), contorted tetrabenzocoronene (cTBC), and contorted tetrabenzofuranylbenzocoronene (cTBFBC) for synthesis and characterization. Our materials characterization found agreement between our calculated and experimental energy values, and through testing of these materials in organic photovoltaic (OPV) devices, we fabricated solar cells with an open-circuit voltage of 1.84 V and an average visible transparency of 88% of the active layer; both quantities exceed previous records for visibly transparent coronene-based solar cells. This work highlights the promise of inverse materials design for future materials discovery, as well as improvements to an exciting application of UV-targeted solar cells.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating Tobin Marks’ 75th Birthday

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...