Spatially heterogeneous epidermal growth factor release from microporous annealed particle (MAP) hydrogel for improved wound closure†
Abstract
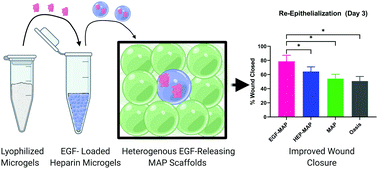
Microporous annealed particle (MAP) hydrogel has been a promising scaffold platform technology to promote immediate tissue integration in injured tissue environments. The addition of growth factors has the potential to accelerate tissue integration and enhance scaffold-mediated healing. Growth factor releasing scaffolds face the translational hurdle of limited solubilized protein shelf stability; however, to address this hurdle we present a lyophilized MAP scaffold which can be effectively rehydrated directly prior to use. Our new approach includes a heterogenous MAP scaffold wherein 5% of the microgels contain immobilized heparin loaded with epidermal growth factor (EGF) at 1 μg mL−1. We demonstrate that these scaffolds, which are directly loaded with EGF following lyophilization maintain equivalent properties to scaffolds loaded passively via diffusion into water-swollen microgels, including EGF release profiles and cell migration studies that did not significantly differ. Further, these heterogeneous scaffolds exhibit a significant increase in cellular migration in vitro and quicker re-epithelialization in vivo. This progress on spatially heterogenous growth factor release from MAP scaffolds has great potential to improve complex wound treatment and advance the field of growth factor releasing scaffolds.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Journal of Materials Chemistry B Emerging Investigators and 2021 Journal of Materials Chemistry B most popular articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...