A sensitive and rapid detection of glutathione based on a fluorescence-enhanced “turn-on” strategy†
Abstract
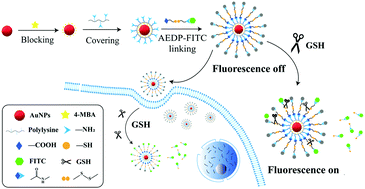
Glutathione (GSH) plays important roles in the human body including protecting cells from oxidative damages and maintaining cellular redox homeostasis. Thus, developing a fast and sensitive method for detecting GSH levels in living bodies is of great importance. Many methods have been developed and used for GSH detection, such as high-performance liquid chromatography, capillary electrophoresis, and fluorescence resonance energy-based methods. However, these methods often lack sensitivity as well as efficiency. Herein, a rapid and sensitive method for glutathione detection was developed based on a fluorescence-enhanced “turn-on” strategy. In this study, a unique and versatile bifunctional linker 3-[(2-aminoethyl) dithio]propionic acid (AEDP)-modified gold nanoparticle (Au@PLL–AEDP–FITC) probe was designed for the simple, highly sensitive intracellular GSH detection, combined with the FRET technique. In the presence of GSH, the disulfide bonds of AEDP on Au@PLL–AEDP–FITC were broken through competition with GSH, and FITC was separated from gold nanoparticles, making the fluorescence signal switch to the “turn on” state. A change in the fluorescence signal intensity has a great linear positive correlation with GSH concentration, in the linear range from 10 nM to 180 nM (R2 = 0.9948), and the limit of detection (LOD) of 3.07 nM, which was lower than other reported optical nanosensor-based methods. Au@PLL–AEDP–FITC also has great selectivity for GSH, making it promising for application in complex biological systems. The Au@PLL–AEDP–FITC probe was also successfully applied in intracellular GSH imaging in HeLa cells with confocal microscopy. In short, the Au@PLL–AEDP–FITC probe-based fluorescence-enhanced “turn-on” strategy is a sensitive, fast, and effective method for GSH detection as compared with other methods. It can be applied in complex biological systems such as cell systems, with promising biological-medical applications in the future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...