Influence of dityrosine nanotubes on the expression of dopamine and differentiation in neural cells†
Abstract
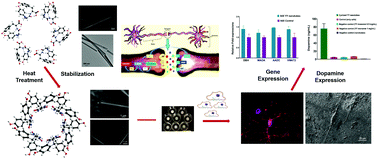
In this study, we report the synthesis of self-assembled dityrosine nanotubes as a biologically functional scaffold and their interactions with neural cells. Quantum chemical methods were used to determine the forces involved in the self-assembly process. The physicochemical properties of the nanostructures relevant to their potential as bioactive scaffolds were characterized. The morphology, secondary structure, crystallinity, mechanical properties, and thermal characteristics of YY nanotubes were analyzed. The influence of these nanotubes as scaffolds for neural cells was studied in vitro to understand their effects on cell proliferation, morphology, and gene expression. The scanning electron microscopy and fluorescence confocal microscopy demonstrated the feasibility of nanotube scaffolds for enhanced adhesion to rat and human neural cells (PC12 and SH-SY5Y). Preliminary ELISA and qPCR analyses demonstrate the upregulation of dopamine synthesis and genes involved in dopamine expression and differentiation. The expression levels of DβH, AADC, VMAT2 and MAOA in SH-SY5Y cells cultured on the nanotube scaffolds for 7 days were elevated in comparison to the control cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...