Dual-responsive polymersomes as anticancer drug carriers for the co-delivery of doxorubicin and paclitaxel†
Abstract
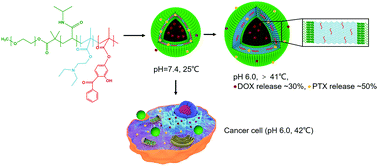
Multi stimuli-responsive polymersomes are in high demand as smart drug carriers, particularly for the treatment of complex cancers. However, most polymersomes have multi-responsiveness that does not affect each other and focus on single drug loading. Here, we have designed photo-crosslinked temperature and pH dual-responsive polymersomes by the self-assembly of a triblock polymer of methoxyl poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-b-poly[2-(diethylamino)ethyl methacrylate-co-2-hydroxy-4-(methacryloyloxy)benzophenone] (mPEG-b-PNIPAM-b-P(DEAEMA-co-BMA)) synthesized via reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT). The dual-responsive polymersomes had a layered membrane, resulting in tunable permeability. Importantly, the polymersomes were proved to have a pH-controlled temperature-responsiveness. A hydrophilic–hydrophobic drug pair (doxorubicin hydrochloride, DOX, and paclitaxel, PTX) could be co-encapsulated in the fabricated polymersomes. The membrane permeability based on its layered structure was triggered by the change in temperature and pH to permit the separate control on the release of DOX and PTX. In a simulated tumor microenvironment, DOX and PTX encapsulated in the polymersomes could take effect for a relatively longer period and could work synergistically. Thus, the photo-crosslinked and dual-responsive polymersomes can be considered as promising drug carriers in the field of tumor combination chemotherapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...