Bioinspired and eco-friendly high efficacy cinnamaldehyde antibacterial surfaces†
Abstract
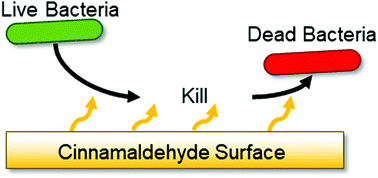
Antimicrobial essential oils are incorporated into mussel-inspired and natural plant polyphenol coatings as part of a single-step fabrication process. Polydopamine–cinnamaldehyde, polyethyleneimine–cinnamaldehyde, and tannic acid–cinnamaldehyde coatings exhibit strong antibacterial activities against both Gram-negative Escherichia coli and Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (with the polydopamine- and tannic acid-based systems displaying log10 Reduction = 8). Cinnamaldehyde impregnation into porous non-woven polypropylene cloth, polytetrafluoroethylene membrane, and knitted cotton cloth also gives rise to high levels of antibacterial activity (log10 Reduction = 8). No loss in antibacterial efficacy is observed for non-woven polypropylene cloth impregnated with cinnamaldehyde over 17 recycle tests.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...