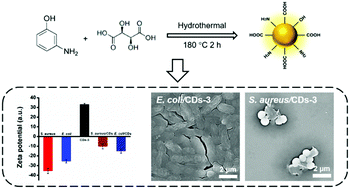
Carbon dots with positive surface charge from tartaric acid and m-aminophenol for selective killing of Gram-positive bacteria†
Abstract
Gram-positive bacteria are one of the most common pathogens causing severe and acute infection, and hospital infection caused by Gram-positive bacteria have increased significantly. Also, as antibiotics have been widely used, abusing of antibiotics is becoming an increasingly serious problem which is followed by dangerous drug resistance. Here, we developed a series of cationic carbon dots (CDs) with high-performance as antibacterial agents by using tartaric acid and m-aminophenol as precursors. The surface charge of these CDs can be regulated from +4.5 ± 0.42 mV to +33.2 ± 0.99 mV by increasing the contents of pyridine N and pyrrolic N in CDs. Further antibacterial experiments show that 250 μg mL−1 of CDs with +33.2 ± 0.99 mV can selectively kill Gram-positive bacteria and the antibacterial efficiency can reach approximately >99%. These CDs with positive surface charge can be selectively absorbed on the cell walls of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) via electrostatic interaction and then disturb their physiological metabolism, eventually leading to bacterial death. The present work provides a novel method to adjust the surface charge of CDs and apply these CDs as alternative antibacterial agents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...