A very mechanically strong and stretchable liquid-free double-network ionic conductor†
Abstract
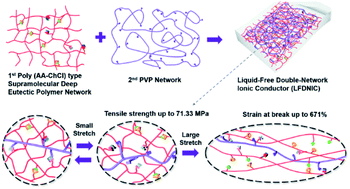
Liquid-free ionic conductors are very desirable for flexible electronics, because hydrogels and ionic liquid-based ionogels suffer from water evaporation and ionic liquid leakage, respectively. However, the development of liquid-free ionic conductors with both high mechanical strength and stretchability remains challenging. In this work, based on the design concept of a double-network, we first report a series of very mechanically strong and tough liquid-free double-network ionic conductors (LFDNICs), consisting entirely of 1st stretchable poly(AA–ChCl) type supramolecular deep eutectic polymer networks and 2nd brittle polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) networks. One of these LFDNICs shows outstanding mechanical performance, with tensile strength, strain at break, and toughness up to 71.3 MPa, 671%, and 268 MJ m−3, respectively. In particular, the LFDNIC can endure puncture and successfully elevate a 10 kg weight (12 500 times its own weight). In addition, the LFDNIC also exhibits promising ionic conductivity (3.1 × 10−4 S m−1), favorable biocompatibility (cell viability up to 97.5%), optimum self-healing properties (electrical healing efficiency of 98% within 0.30 s), and adequate transparency (92% in the visible range). Due to their practical features and exceedingly simple preparation process, we believe that LFDNICs will not only provide an innovative prospect for the development of mechanically-strong ionic conductors, but can also be further researched and used in the fields of advanced sensors and flexible electronic devices.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Journal of Materials Chemistry A Lunar New Year collection 2022 and 2021 Journal of Materials Chemistry A most popular articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...