An over 20% solar-to-hydrogen efficiency system comprising a self-reconstructed NiCoFe-based hydroxide nanosheet electrocatalyst and monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cell†
Abstract
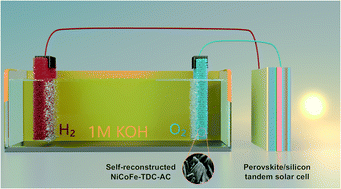
Using only low-cost materials to achieve a solar-to-hydrogen (STH) efficiency of over 20% for solar water splitting systems is still a major challenge for realizing the practical feasibility of photoelectrochemical (PEC) hydrogen production technology. Utilizing the electrochemical instability of some metal organic framework ligands is a promising strategy to solve the problem of difficulty in controlling the degree of electrochemical self-reconstruction and obtaining high-performance water oxidation catalysts. Here, a monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cell was used for highly efficient standalone solar water splitting. A self-reconstructed NiCoFe-based hydroxide nanosheet electrocatalyst was shown to exhibit remarkable oxygen evolution reaction performance with an overpotential of 191 mV at 10 mA cm−2. Upon pairing with the reported state-of-the-art hydrogen evolution reaction catalyst NiMo4/MnO3−X and a monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cell, an unprecedented STH efficiency of 21.32% was achieved for the unbiased solar water splitting system. This low-cost high-efficiency solar water-splitting system will contribute to realizing the practical applications of PEC hydrogen production technology.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editor’s Choice: Perovskite-based solar cells


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...