Biomass-derived tubular carbon materials: progress in synthesis and applications
Abstract
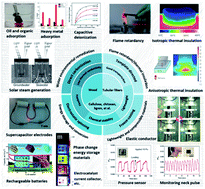
Tubular structures are unique naturally occurring morphologies that are the result of trillions of years of evolution. These structures can provide low density and minimal thermal conductivity, all of which are important advantages in harsh natural environments, and can also promote the transport of water and nutrients. In view of the intrinsic advantages of biomass-derived carbon materials, including their sustainability, porous structures, high conductivity, hydrophobicity, ready modification and chemical stability, such materials with tubular structures may show even better performance. Inspired by these unique properties, various studies of biomass-derived tubular carbon materials (BTCMs) have fabricated specimens showing exceptional performance. In this review, we provide a timely overview of the advantages of tubular structures and also discuss strategies for preparing BTCMs by various routes, including efficient top-down direct carbonization from tubular fibers or wood and more controllable bottom-up assembly from building blocks such as cellulose, lignin, and chitosan. The hard-template synthesis, freeze casting and electrostatic spinning methods are all examined. Potential applications of BTCMs are also discussed, including those in environmental remediation, energy storage and conversion, and the production of lightweight compressible materials and thermal insulating materials. Finally, the current challenges within the field of BTCMs are highlighted, and the future prospects for the fabrication of truly high-performance functional carbon materials from biomass are summarized.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...