Physical and chemical activation mechanisms of carbon materials based on the microdomain model†
Abstract
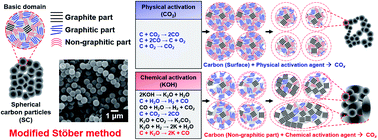
Physical and chemical activation mechanisms of carbon materials are investigated. Uniformly sized spherical carbon particles (SCs) are preferentially synthesized using a modified Stöber method and activated under various activation conditions. To elucidate the activation mechanisms, we carefully examine changes in the morphologies, physical properties, and crystallinities of the SCs due to activation under each set of conditions. In addition, we apply the activated SCs (ASCs) to electrode materials for electric double-layer capacitors, and double-check the characteristics of the ASCs from confirmation of their electrochemical properties. Physical carbon activation mainly proceeds via the non-selective removal of carbon from the SC surfaces. Various reactions occurring within the carbon particles during chemical activation selectively remove non-graphitic parts. In the case of the physical activation method, a high activation temperature is required to obtain highly porous carbon with a large surface area. Thus, a relatively high degree of burn-off is inevitable. In contrast, chemical activation at comparatively low temperatures rapidly converts the SCs into highly porous activated carbon. Furthermore, crystallinity is gradually enhanced by the selective removal of non-graphitic parts at higher activation temperatures. Based on these results, we are able to propose mechanisms for the physical and chemical activation of carbon materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...