Controlling surface chemistry and mechanical properties of metal ionogels through Lewis acidity and basicity†
Abstract
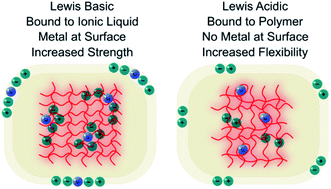
Ionogels are emerging as soft materials with remarkable physical properties that can be tuned to suit application requirements. The liquid component—ionic liquids—are effectively involatile, which provides new opportunities to explore gel surfaces with UHV based analytical techniques. Here, we exploit the highly solvating nature of ionic liquids to fabricate poly(ethylene glycol) based ionogels with high concentrations of zinc, and then investigate their surfaces to show that tunability extends beyond the bulk to the interface. A unique relationship between Lewis acidity and basicity and the surface concentration of metal was revealed. Chemical state analysis and molecular dynamics showed that Lewis acidic metals templated polymers to give new architectures reduced brittleness and increased flexibility, while Lewis basic metals improved polymer uniformity and strengthened gels. Therefore, bulk structure, surface composition, and metal speciation were all found to be intimately related and dependent upon the coordination strengths of ionic liquid anions. Importantly, the highly controllable surface and structural properties of metal ionogels allow fine-tuning across a broad design space, which presents new opportunities for gel based applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...