Recyclable, weldable, mechanically durable, and programmable liquid metal-elastomer composites†
Abstract
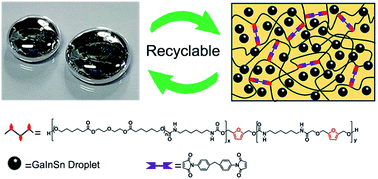
Liquid metal (LM)-based elastomers have received growing interest for a wide range of applications spanning from soft robotics to flexible electronics. However, the fabrication of multifunctional LM-based elastomers, in particular, featuring recyclability and transience while simultaneously offering excellent mechanical performance and stability, remains a challenge. Herein, we report a strategy for the fabrication of durable and recyclable multifunctional LM elastomer composites, which consist of LM droplets as functional fillers and Diels–Alder (DA) bond crosslinked polyurethane (PU) networks as the polymer matrix. The composite shows good mechanical properties and can be spatially tuned from an electrical insulator to a conductor through a so-called “mechano-training” process. The mechano-trained composite exhibits extraordinarily stable electrical performance even after 10 000 stretching–releasing cycles at 100% tensile strain. The DA bond-crosslinked network endows the composite with good self-healing properties, high freedom in (re)programming of 3D shapes, and favorable transience. Moreover, spatially thermal and photothermal heating enables the repair/welding of broken circuits or programming of intricate shapes. Besides, the composite can be swiftly destructed by dissolution at an elevated temperature while the valuable LM can be retrieved at a yield of 89%. The multifunctionality, good mechanical and electrical performance, and in particular transience render this composite an environmentally friendly material for flexible transient electronics, actuators, and wearable devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...