Deep indentation and puncture of a rigid cylinder inserted into a soft solid†
Abstract
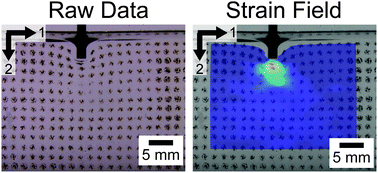
Deep indentation and puncture can be used to characterize the large strain elastic and fracture properties of soft solids and biological tissues. While this characterization method is growing in application there are still open questions about deep indentation and puncture, including how the distribution of strains and stresses in the surrounding material relate to the resultant force exerted on the indenter. Direct quantification of the deformation field around a rigid indenter during penetration of a soft solid is necessary to substantiate the current qualitative understanding of these strains and increase the impact and usefulness of puncture tests. Here, the deformation field of a rigid cylinder inserted into a soft solid is quantified using digital image correlation (DIC). DIC measurements are validated by reconstituting the measured nominal force on the cylinder during deep indentation and puncture. The deformation field is used to map the strain field around the indenter during deep indentation and puncture. These measurements provide direct insight into the puncture process and show that while the resultant force mainly arises from the sheared region on the sides of the indenter, the compressed region below the tip is responsible for initiating failure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...