Structure, dynamics, and morphology of nanostructured water confined between parallel graphene surfaces and in carbon nanotubes by applying magnetic and electric fields†
Abstract
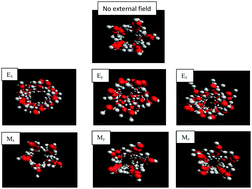
Water molecules experience certain changes in their properties when they feel an external magnetic or electric field. These changes are significant in different applications, such as biological and biotechnological processes, nano-pumping, and water treatment. In this work, we have performed molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to investigate the different thermodynamics, structure, and dynamics of water molecules confined between two parallel surfaces and also confined in carbon nanotubes (CNTs). We have also applied different electric and magnetic fields in different directions to the confined molecules. In the graphene system, no polygonal shape was formed in either low or high electric fields, whereas rhombic and pentagonal shapes were formed in low and high magnetic fields. In the CNT system, applying electric fields in all three dimensions made the pentagonal shape disappear and the confined water molecules formed a ring shape when the electric field was applied in the axial direction. Applying the electric field perpendicular to the graphene surfaces increases the self-diffusion of the confined molecules, whereas applying the electric and magnetic fields along the CNT axis decreases the self-diffusion of the confined water molecules. In the graphene system, applying the electric field perpendicular to the graphene surfaces decreases the average number of hydrogen bonds (〈HB〉) whereas the magnetic field has little effect on the 〈HB〉. In the CNT system, applying Ex also leads to a smaller number of HBs. Also, applying the magnetic field along the x-direction (along the CNT direction) leads to a greater number of HBs than the other fields.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...